
Section 1: Properties of Bromine
Reference Source:- Kirk Othmer Encyclopaedia of Chemical Technology 3rd Edition 1978 (Except where otherwise stated).
- Boiling Point: 58.8°C
- Freezing Point: -7.25°C
- Molecular weight: 159.8
| Density of Liquid Bromine (g/ml) | |
| 15°C | 3.1396 |
| 20°C | 3.1226 |
| 25°C | 3.1055 |
- Viscosity, 20°C, Centistokes: 0.31 (1)
- Vapour Density (air = 1) at Boiling Point: 5.5 (2)
- Vol Coeff of Expansion (20 – 30°C) 0.0011 per °C
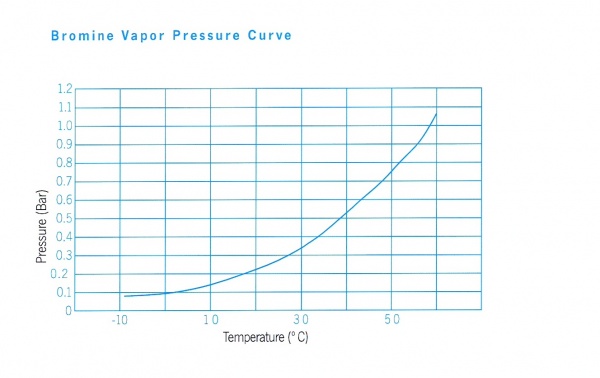
- Vapour Pressure, 175 mmHg (20°C)
- Latent Heat of Vaporisation (Boiling Point) 187 kJ/kg (44.8 cal/g)
- Specific Heat of Liquid (25°C): 0.473 Kj/kg/°C (2) (0.113 cal/g/°C; 18.09 cal/mole/°C)
- Solubility in water at 20°C: 3.41g/100g
- Solubility of water in bromine at 20°C: 34 mg/100g
- Entropy, liquid, cal/mole °K, 25°C: 36.4 (1)
- Dielectric Constant, 10^5 freq., 25°C: 3.33 (1)
- Surface tension, dynes/cm, 58.6°C: 36 (1)
- Flash point: none
- Fire point: none
- Refractive index, 15°C/D: 1.661 (1)
- Compressibility, saturated vapours, PV/RT, 25°C: 0.991 (1)
Two physical properties of bromine can be exploited to reduce evolution of fumes from a spillage, namely its density and its limited solubility in water. Laboratory tests carried out by ICI have indicated that evolution of fumes from liquid bromine caught in a water filled bund or contained and covered by a layer of water from a drenching system is suppressed by 99%.
Additional References
- Bromine Handling Manual, Albemarle 1995
- Occupational Health Guidelines for Bromine. US Dept of Labour 1978.
- Hildebrand et al.; Journal American Chemical Society 80, 4129 (1958).
Bromine is highly reactive and a strong oxidising agent. It will react vigorously with reducing agents and many organic materials, including solvents. Although bromine is not itself combustible, the heat of reaction is sufficient to initiate combustion when in contact with phosphorus or sulphur. Dry loose flammable material such as paper and wood shavings can be similarly ignited, and liquid bromine will attack some plastics and rubber.
Dry bromine will react violently with aluminium, titanium, mercury and alkali metals apart from sodium, but is not generally reactive with other metals. Reactivity is, however, markedly increased by traces of water or some organic impurities. Relatively few metals are resistant to moist bromine.
Bromine is very hygroscopic. Dry bromine rapidly absorbs water from the atmosphere. It is therefore advisable, except under well defined circumstances, to treat all bromine as being moist.
| Wet (1) | Dry (Below 30 mg/kg) | |||
| Gas | Liquid | Gas | Liquid | |
| Metals | ||||
| Lead (2) (3) (4) | at 25°C | G | up to 50°C | |
| Tantalum (3) | G | up to 200°C | G | up to 200°C |
| Mild Steel, Cast Iron | U | U | U | U |
| Aluminium/Adluminium Alloys | U | U | U | U |
| Stainless Steels (Austenitic) | U | U | S(5) | S(5) |
| Nickel, Monel | U | U | G | G |
| Inconel | U | U | ||
| Hastelloy “C” | U | U | G | G |
| Copper, Brass | U | U | U | U |
| Bronze | U | U | ||
| Silver | U | U | ||
| Titanium | [S(5)] | U | U | U |
| Niobium and Niobium/Tantalum Alloy | ||||
| Ceramics | ||||
| Stoneware, Porcelain, Glass (6) | G | G | G | G |
| Plastics | ||||
| PTFE, PCTFE, PVDF, FEP (7) | G | G | G | G |
| Ebonite | U | U | U | U |
| CPVC, PVC | U | U | U | U |
| Polyethylene, Polypropylene | U | U | U | U |
- The resistance to wet bromine depends upon the water content and temperature. Bromine in contact with air of 80% relative humidity can pick up 300 mg of water per litre.
- Chemical Lead, BS 334: 1983 (type A).
- Data refer to gas or liquid.
- Tin-free flux should be used for lead burning.
- Only if found satisfactory after specific trials. Evidence on titanium is conflicting and it should be contemplated for use only with wet bromine gas and then with caution.
- Upper temperature limit is determined by factors other than corrosion. Avoid mechanical or thermal shock.
- Notes on the Selection and Use of Fluorocarbon Polymers
Services
Handbook
The purpose of this document is to provide information and guidance to both bromine users and trained response personnel. The manual contains technical facts, engineering detail, health information and media response data.
